📝Life Processes (Question Bank)
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect?
(a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll
(b) They store carbohydrates in the form of starch
(c) They convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates in
the absence of sunlight
(d) They constitute the first trophic level in food chains
Ans: (c)
2. In which of the following groups of organisms, the food material is broken down outside the body and absorbed?
(a) Mushroom, green plants, Amoeba
(b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould
(c) Paramecium, Amoeba, Cuscuta
(d) Cuscuta, lice, tapeworm
Ans: (b)
3. Select the correct statement
(a) Heterotrophs do not synthesise their own food
(b) Heterotrophs utilise solar energy for photosynthesis
(c) Heterotrophs synthesise their own food
(d) Heterotrophs are capable of converting carbon dioxide and
water into carbohydrates
Ans: (a)
4. If salivary amylase is lacking in the saliva, which of the following events in the mouth cavity will be affected?
(a) Proteins breaking down into amino acids
(b) Starch breaking down into sugars
(c) Fats breaking down into fatty acids and glycerol
(d) Absorption of vitamins
Ans: (b)
5. The inner lining of stomach is protected by one of the following from hydrochloric acid. Choose the correct one
(a) Pepsin
(b) Mucus
(c) Salivary amylase
(d) Bile
Ans: (b)
6. Which is the correct sequence of parts in the human alimentary canal?
(a) Mouth `rightarrow` stomach `rightarrow` small intestine `rightarrow` oesophagus`rightarrow` large intestine
(b) Mouth `rightarrow` oesophagus `rightarrow` stomach `rightarrow`large intestine`rightarrow` small intestine
(c) Mouth `rightarrow` stomach `rightarrow` oesophagus `rightarrow` small intestine `rightarrow`large intestine
(d) Mouth `rightarrow` oesophagus `rightarrow` stomach `rightarrow` small intestine `rightarrow` large intestine
Ans: (d)
7. Which part of the alimentary canal receives bile from the liver?
(a) Stomach
(b) Small intestine
(c) Large intestine
(d) Oesophagus
Ans: (b)
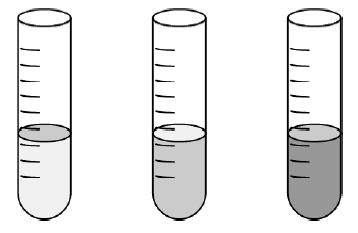
8. A few drops of iodine solution were added to rice water. The solution turned blue-black in colour. This indicates that rice water contains
(a) complex proteins
(b) simple proteins
(c) fats
(d) starch
Ans: (d)
9. In which part of the alimentary canal food is finally digested?
(a) Stomach
(b) Mouth cavity
(c) Large intestine
(d) Small intestine
Ans: (d)
10. Choose the function of the pancreatic juice from the following
(a) trypsin digests proteins and lipase carbohydrates
(b) trypsin digests emulsified fats and lipase proteins
(c) trypsin and lipase digest fats
(d) trypsin digests proteins and lipase emulsified fats
Ans: (d)
11. When air is blown from the mouth into a test tube containing lime water, the lime water turned milky due to the presence of
(a) oxygen
(b) carbon dioxide
(c) nitrogen
(d) water vapour
Ans: (b)
12. The correct sequence of anaerobic reactions in yeast is
13. Which of the following is most appropriate for aerobic respiration?
14. Which of the following statement(s) is (are) true about respiration?
(i) During inhalation, ribs move inward and diaphragm is raised
(ii) In the alveoli, exchange of gases takes place i.e., oxygen from alveolar air diffuses into blood and carbon dioxide from blood into alveolar air
(iii) Haemoglobin has greater affinity for carbon dioxide than oxygen
(iv) Alveoli increase surface area for exchange of gases
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans: (d)
15. Which is the correct sequence of air passage during inhalation?
(a) Nostrils `rightarrow` larynx `rightarrow` pharynx `rightarrow` trachea `rightarrow` lungs
(b) Nasal passage `rightarrow` trachea `rightarrow` pharynx `rightarrow` larynx `rightarrow` alveoli
(c) larynx `rightarrow` nostrils `rightarrow` pharynx `rightarrow` lungs
(d) Nostrils `rightarrow` pharynx `rightarrow` larynx `rightarrow` trachea `rightarrow` alveoli
Ans: (d)
16. During respiration exchange of gases take place in
(a) trachea and larynx
(b) alveoli of lungs
(c) alveoli and throat
(d) throat and larynx
Ans: (b)
17. Which of the following statement (s) is (are) true about heart?
(i) Left atrium receives oxygenated blood from different parts of body while right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from lungs
(ii) Left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to different body parts while right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs
(iii) Left atrium transfers oxygenated blood to right ventricle which sends it to different body parts
(iv) Right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from different parts of the body while left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to different parts of the body
(a) (i)
(b) (ii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Ans: (c)
18. What prevents backflow of blood inside the heart during contraction?
(a) Valves in heart
(b) Thick muscular walls of ventricles
(c) Thin walls of atria
(d) All of the above
Ans: (a)
19. Single circulation i.e., blood flows through the heart only once during one cycle of passage through the body, is exhibited by
(a) Labeo, Chameleon, Salamander
(b) Hippocampus, Exocoetus, Anabas
(c) Hyla, Rana, Draco
(d) Whale, Dolphin, Turtle
Ans: (b)
20. In which of the following vertebrate group/groups, heart does not pump oxygenated blood to different parts of the body?
(a) Pisces and amphibians
(b) Amphibians and reptiles
(c) Amphibians only
(d) Pisces only
Ans: (d)
21. Choose the correct statement that describes arteries.
(a) They have thick elastic walls, blood flows under high pressure; collect blood from different organs and bring it back to the heart
(b) They have thin walls with valves inside, blood flows under low pressure and carry blood away from the heart to various
organs of the body
(c) They have thick elastic walls, blood flows under low pressure; carry blood from the heart to various organs of the body
(d) They have thick elastic walls without valves inside, blood flows under high pressure and carry blood away from the heart to different parts of the body.
Ans: (d)
22. The filtration units of kidneys are called
(a) ureter
(b) urethra
(c) neurons
(d) nephrons
Ans: (d)
23. Oxygen liberated during photosynthesis comes from
(a) water
(b) chlorophyll
(c) carbon dioxide
(d) glucose
Ans: (a)
24. The blood leaving the tissues becomes richer in
(a) carbon dioxide
(b) water
(c) heamoglobin
(d) oxygen
Ans: (a)
25. Which of the following is an incorrect statement?
(a) Organisms grow with time
(b) Organisms must repair and maintain their structure
(c) Movement of molecules does not take place among cells
(d) Energy is essential for life processes
Ans: (c)
26. The internal (cellular) energy reserve in autotrophs is
(a) glycogen
(b) protein
(c) starch
(d) fatty acid
Ans: (c)
27. Which of the following equations is the summary of photosynthesis?
(a) `6CO_2 + 12H_2O rightarrow C_6H_12O_6 + 6O_2+ 6H_2O`
(b) `6CO_2 + H_2O +` Sunlight `rightarrow C_6H_12O_6 + O_2+ 6H_2O`
(c) `6CO_2 + 12H_2O +` Chlorophyll + Sunlight `rightarrow C_6H_12O_6 + 6O_2+ 6H_2O`
(d) `6CO_2 + 12H_2O +` Chlorophyll + Sunlight `rightarrow C_6H_12O_6 + 6CO_2+ 6H_2O`
Ans: (c)
28. Choose the event that does not occur in photosynthesis
(a) Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll
(b) Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates
(c) Oxidation of carbon to carbon dioxide
(d) Conversion of light energy to chemical energy
Ans: (c)
29. The opening and closing of the stomatal pore depends upon
(a) oxygen
(b) temperature
(c) water in guard cells
(d) concentration of `CO_2` in stomata
Ans: (c)
30. Choose the forms in which most plants absorb nitrogen
(i) Proteins
(ii) Nitrates and Nitrites
(iii) Urea
(iv) Atmospheric nitrogen
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Ans: (b)
31. Which is the first enzyme to mix with food in the digestive tract?
(a) Pepsin
(b) Cellulase
(c) Amylase
(d) Trypsin
Ans: (c)
32. Which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
(i) Pyruvate can be converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide by yeast
(ii) Fermentation takes place in aerobic bacteria
(iii) Fermentation takes place in mitochondria
(iv) Fermentation is a form of anaerobic respiration
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Ans: (c)
33. Lack of oxygen in muscles often leads to cramps among cricketers. This results due to
(a) conversion of pyruvate to ethanol
(b) conversion of pyruvate to glucose
(c) non conversion of glucose to pyruvate
(d) conversion of pyruvate to lactic acid
Ans: (d)
34. Choose the correct path of urine in our body
(a) kidney `rightarrow` ureter `rightarrow` urethra `rightarrow` urinary bladder
(b) kidney `rightarrow` urinary bladder `rightarrow` urethra `rightarrow` ureter
(c) kidney `rightarrow` ureters `rightarrow`urinary bladder `rightarrow` urethra
(d) urinary bladder `rightarrow` kidney `rightarrow` ureter `rightarrow` urethra
Ans: (c)
35. During deficiency of oxygen in tissues of human beings, pyruvic acid is converted into lactic acid in the
(a) cytoplasm
(b) chloroplast
(c) mitochondria
(d) golgi body
Ans: (a)
36. Carefully study the diagram of the human respiratory system with labels A, B, C and D. Select the option which gives correct identification and main function and /or characteristic
(a). (i) Trachea: It is supported by bony rings for conducting inspired air.
(b). (ii) Ribs: When we breathe out, ribs are lifted.
(c). (iii) Alveoli: Thin-walled sac-like structures for exchange of gases.
(d). (iv) Diaphragm: It is pulled up when we breathe in.
Ans: (c)
37. Identify the option that indicates the correct enzyme that is secreted in location A, B and C.
(a). (i)-lipase, (ii)-trypsin, (iii)-pepsin
(b). (i)-amylase, (ii)-pepsin, (iii)-trypsin
(c). (i)-trypsin, (ii)-amylase, (iii)-carboxylase
(d). (i)-permease, (ii)-carboxylase, (iii)-oxidase
Ans: (b)
38. Observe the diagram of Human digestive system.
(b). i.- b) ; ii – c) ; iii – d) ; iv- a)
(c). i.- b) ; ii – d) ; iii – c) ; iv- a)
(d). i.- d) ; ii – a) ; iii – b) ; iv- c)
Ans: (b)
39. The figure given below shows a schematic plan of blood circulation in humans with labels (i) to (iv). Identify the correct label with its functions?
B. (ii) Pulmonary artery - takes blood from lung to heart.
C. (iii) Aorta - takes blood from heart to body parts.
D. (iv) Vena cava takes - blood from body parts to right auricle.
Ans: (D)
40. Identify the phase of circulation which is represented in the diagram of heart given below. Arrows indicate contraction of the chambers shown.
A. Blood transferred to the right ventricle and left ventricle simultaneously.
B. Blood is transferred to lungs for oxygenation and is pumped into various organs simultaneously.
C. Blood transferred to the right auricle and left auricle simultaneously.
D. Blood is received from lungs after oxygenation and is received from various organs of the body.
Ans: (B)
41. What is common between extensive network of blood vessels around walls of alveoli and in glomerulus of nephron?
A. Thick walled arteries richly supplied with blood
B. Thin walled veins poorly supplied with blood
C. Thick walled capillaries poorly supplied with blood.
D. Thin walled capillaries richly supplied with blood
Ans: (D)
42. Given below are the functions of some parts of human circulatory system. Identify the correct match.
A. Pulmonary vein – takes oxygenated blood from body partsto heart
B. Artery – takes oxygenated blood from heart to lung
C. Dorsal aorta – takes deoxygenated blood from heart to body parts
D. Vena cava – takes deoxygenated blood from body parts to right atrium
Ans: (D)
43. Identify the option that indicates the correct enzyme that is secreted in location L, M and N.L, M and N represent Mouth cavity, stomach and small intestine of the human being.
44. What happens when right and left ventricle contract during pumping of blood by human heart?
A. Blood transferred to the right ventricle and left ventricle simultaneously.
B. Blood is transferred to lungs for oxygenation and is pumped into various organs simultaneously.
C. Blood transferred to the right atrium and left atrium simultaneously.
D. Blood is received from lungs after oxygenation and is received from various organs of the body.
Ans: (B)
45. i, ii, iii and iv represent mouth cavity, liver, first part of small intestine and complete small intestine respectively of Human digestive system. Match the labeling referred in column I andcorrelate with the function in column II.
B. i.- b ; ii – c ; iii – d ; iv- a
C. i.- a ; ii – c ; iii – d ; iv- c
D. i.- d ; ii – a ; iii – b ; iv- c
Ans: (B)
46. An incomplete equation for the digestion of starch using saliva is shown as:
Saliva + Starch (in test tube) →
What will be the likely outcome of this?
(a) Saliva will convert starch into complex fat molecules.
(b) Saliva will convert starch into complex sugar molecules.
(c) Saliva will breakdown starch into simple sugar molecules.
(d) Saliva will breakdown starch into simple protein molecules.
Ans: (c)
47. A student sets up an experiment to study the role of enzymes in digestion of food.
In which test tube, the digestion of protein will occur?
(a) Test tube A as pepsin will breakdown into simple molecules.
(b) Test tube B as HCl will breakdown protein into simple molecules.
(c) Test tubes A as pepsin will breakdown protein into simple molecules.
(d) Test tube B as HCl will activate pepsin for breakdown of protein into simple molecules.
Ans: (b)
48. The image shows the flow diagram for the breakdown of glucose in yeast.
Under which condition these types of products are obtained?
(a) in the presence of oxygen
(b) in the absence of oxygen
(c) the presence of carbon dioxide
(d) in the absence of carbon dioxide
Ans: (b)
49. How water is taken up from soil to the xylem tissue of the plant roots?
(a) xylem attracts water molecules
(b) roots act as a suction pump for taking water
(c) soil expels the water with pressure to the xylem
(d) difference in the ion concentration creates a gradient for water movement
Ans: (d)
50. The loss of water from the leaves of the plant is transpiration. How this process is advantageous for the plant?
(a) It helps in the downward movement of the water.
(b) It helps the plant to maintain temperature in hot sunny days.
(c) It acts as a driving force for distribution of food in plant’s body.
(d) helps maintain a constant level of water in the soil around the plant
Ans: (b)
51. A plant gets rid of excess water through transpiration. Which is a method used by plants to get rid of solid waste products?
(a) shortening of stem
(b) dropping down of fruits
(c) shedding of yellow leaves
(d) expansion of roots into the soil
Ans: (c)
★★★★★★
Case Studies
1. The Figure shown below represents an activity to prove the requirements for photosynthesis. During this activity, two healthy potted plants were kept in the dark for 72 hours. After 72 hours, KOH is kept in the watch glass in setup X and not in setup Y. Both these setups are air tight and have been kept in light for 6 hours. Then, Iodine Test is performed with one leaf from each of the two plants X and Y.
(i) This experimental set up is used to prove essentiality of which of the following requirements of photosynthesis?
A. Chlorophyll
B. Oxygen
C. Carbon dioxide
D. Sunlight
Ans: (C)
(ii) The function of KOH is to absorb
A. Oxygen.
B. Carbon dioxide.
C. Moisture.
D. Sunlight
Ans: (B)
(iii) Which of the following statements shows the correct results of Iodine Test performed on the leaf from plant X and Y respectively?
A. Blue - black colour would be obtained on the leaf of plant Xand no change in colour on leaf of plant Y.
B. Blue - black colour would be obtained on the leaf of plant Y and no change in colour onleaf of plant X.
C. Red colour would be obtained on the leaf of plant X and brown colour on the leaf of plant Y.
D. Red colour would be obtained on the leaf of plant Y and brown colour on the leaf of plant X
Ans: (B)
(iv)Which of the following steps can be followed for making the apparatus air tight?
i. placing the plants on glass plate
ii. using a suction pump.
iii. applying aseline to seal the bottom of jar.
iv. creating vacuum
A. i and ii
B. ii. and iii
C. i. and iii
D. ii. and iv
Ans: (C)
2. Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) All living cells require energy for various activities. This energy is available by the breakdown of simple carbohydrates either using oxygen or without using oxygen.
(i) Energy in the case of higher plants and animals is obtained by
a) Breathing
b) Tissue respiration
c) Organ respiration
d) Digestion of food
Ans: (b)
(ii) The graph below represents the blood lactic acid concentration of an athlete during a race of 400 m and shows a peak at point D.
Lactic acid production has occurred in the athlete while running in the 400 m race. Which of the following processes explains this event?
a) Aerobic respiration
b) Anaerobic respiration
c) Fermentation
d) Breathing
Ans: (b)
(iii) Study the graph below that represents the amount of energy supplied with respect to the time while an athlete is running at full speed.
(iv) The characteristic processes observed in anaerobic respiration are
i) presence of oxygen
ii) release of carbon dioxide
iii) release of energy
iv) release of lactic acid
a) i) ,ii) only
b) i), ii), iii) only
c) ii), iii), iv) only
d) iv) only
Ans: (c)
(v) Study the table below and select the row that has the incorrect information
Ans: (a)
3. The image shows the circulation of blood in fishes and humans
How is the circulations of blood in fish different from that in humans?
(a) The heart in fish is bigger in size.
(b) The flow of blood in fish is unidirectional.
(c) The blood goes through heart only once in fishes.
(d) The heart of fish has more chambers compared to that of a human.
Ans: (c)
4. The image shows the healing of a wound.
Based on the image, what explains the process?
(a) platelets form clot by plugging the site of injury
(b) platelets uses component of broken vessel to form clot
(c) red blood cells divide and replace the broken vessel at the site of injury
(d) red blood cells and platelets migrate to site of injury and secrete substance that forms new vessel
Ans: (a)
5. The image shows the process of making food by a plant.
Which statement can be concluded from the image?
(a) plants absorb `CO_2` from air and `H_2O` from the soil as raw materials and convert them into glucose
(b) plants absorb `CO_2` from the soil and `H_2O` from air as raw materials and convert them into glucose
(c) plants absorb `O_2` from air and glucose from the soil as raw materials and convert them into light energy
(d) plants absorb `O_2` from air and minerals from the soil as raw materials and convert them into heat energy
Ans: (a)
6. A student sets up an experiment to study the importance of nutrition in plants. The student takes 2 pots, pot 1 and pot 2 each with the same healthy plant. Both the pots were placed in the garden and watered properly. Pot 1 was kept as such, while pot 2 was kept in an air-tight glass box with caustic soda. Caustic soda absorbs carbon dioxide present in the surrounding. After 2 days, the student observes that the plant kept in the garden is healthy while the plant is placed in a container shed leaves and droops. What is the likely reason for this observation?
(a) lack of nutrients in the soil
(b) absence of oxygen for survival
(c) inability to perform photosynthesis
(d) absorption of light by caustic soda restricting growth
Ans: (c)
7. Which of the equation show correct conversion of CO2 and H2O into carbohydrates in plants?
Ans: (c)8. A student sets up an experiment to study photosynthesis in plants. The student de-starched a potted plant by keeping it in a dark room for 3 days. Half of the portion of de-starched leaf was placed in a bottle containing caustic potash (absorbs `CO_2`) as shown
The student then places the plant in light and tests the leaf after 5 hours for the presence of starch. The portions inside the bottle shows negative starch test by reflecting no change in colour when react with iodine, however, other upper portions of the leaf gave positive starch test showing blue-black colour with iodine. What can be evaluated from this experiment?
(a) carbon dioxide is directly linked with the colour of leaf
(b) carbon dioxide is necessary for preparing carbohydrate
(c) lack of carbon dioxide increases amount of starch in plant
(d) lack of carbon dioxide slows the process of photosynthesis
Ans: (b)
9. The image shows the bread moulds on a bread.
How this process is advantageous for Amoeba?
(a) capturing of food takes less time
(b) complex food can be digested easily
(c) more amount of food can be consumed
(d) fast distribution of nutrition within the body
Ans: (d)
11. The image shows the human digestive system.
Digestion of food starts from which organ of the digestive system?
(a) mouth due to the presence of saliva
(b) oesophagus that moves the food in gut
(c) that releases juices for fat breakdown
(d) which helps in mixing food with digestive juices
Ans: (a)
12. The image shows a cross section of small intestine.
What will be the likely happen if the number of villi increases in the intestine?
(a) increase in the absorption of food
(b) fast elimination of waste from the body
(c) increase in flow of blood in the small intestine
(d) fast breakdown of larger food particles into smaller ones
Ans: (a)
13. Which pathway will occur in the cell of an athlete who is performing 100m sprint?
Ans: (c)
After 10 minutes, the student observes that the candle in flask A extinguish faster while candle in flask B keeps burning for a longer time. What can be evaluated from this experiment?
(a) candle produces high amount of carbon dioxide
(b) living beings consumes oxygen during respiration
(c) burning of candle decreases the life span of cockroach
(d) water vapours produced by living beings prevents burning of candle
Ans: (b)
15. A student sets up an experiment to study human respiration using lime water, test tube and a straw. Lime water is colourless in the absence of `CO_2` and is milky in its presence. The student fills a freshly prepared limewater in a test tube and blows air through straw into the limewater. It was observed that the solution turns cloudy as shown.
What can be evaluated from this observation?
(a) oxygen is exhaled during respiration
(b) glucose is produced during respiration
(c) carbon dioxide is exhaled during respiration
(d) water vapours are produced during respiration
Ans: (c)
16. The image shows the process of photosynthesis in plants
Based on the image, which component is excreted by plants during photosynthesis?
(a) Carbon dioxide
(b) Glucose
(c) Light energy
(d) Oxygen
Ans: (d)
17. The image shows the structure of a nephron.
Nephron is a unit of filtration in kidneys that filters waste material. It selectively reabsorbs or excretes water with the help of capillaries that surround it. What is the likely benefit of this?
(a) It makes the process of filtration at Bowman’s capsule easier.
(b) It helps keep the output of urine constant throughout the day.
(c) It helps to uptake and store excess amount of water in the body for later use.
(d) It maintains the concentration of urine based on the amount of water present in the
body.
Ans: (d)
18. The image shows the excretory system in humans
What is the importance of the labelled part in excretory system?
(a) It produces urine.
(b) It filters waste from the blood.
(c) It stores the urine till urination.
(d) It carries urine from kidney to outside.
Ans: (c)
19. The image shows the transport of gases in body through heart and lungs.
Which option correctly shows the transport of oxygen to the cell?
(a) Lungs → pulmonary vein → left atrium →left ventricle → aorta → body cells
(b) Lungs → pulmonary vein → right atrium →right ventricle → aorta → body cells
(c) Lungs → pulmonary artery → left atrium → left ventricle → vanacava → body cells
(d) Lungs → pulmonary artery →right atrium → right ventricle→ vanacava → body cells
Ans: (a)
20. The image shows oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood in the human heart.
What is the direction of deoxygenated blood from right atrium of the heart?
(a) towards the lungs
(b) towards the lower body
(c) towards the upper body
(d) towards the left atrium of heart
Ans: (a)
21. The image shows the circulation of blood in fishes.
Which option correctly traces the pathway of blood flow in fish body?
(a) Gill capillaries→ oxygenated blood→ heart → body cells→ deoxygenated blood→ gills
(b) Gill capillaries→ oxygenated blood→ body cells→ deoxygenated blood→ heart→gills
(c) capillaries→ heart → oxygenated blood→ body cells→ deoxygenated blood→ heart→ gills
(d) Gill capillaries→ oxygenated blood→ heart → body cells→ deoxygenated blood→ heart→gills
Ans: (b)22. The image shows the structure of an artery
(a) to carry large amount of blood
(b) to allow easy exchange of gases with cells
(c) to ensure blood flows in only one direction
(d) to sustain the high-pressure blood from the heart
Ans: (d)
23. A student performs an experiment using a balsam plant with intact stem, leaves, roots and flowers. The plant was kept in a test tube containing eosin solution (a pink colour dye). The test tube mouth was covered using cotton plug as shown.
The student kept the plant undisturbed in the lab. After 2-3 hours, a transverse section of stem was obtained using sharp scissors and studied under microscope. The studies reveal the presence of pink colour in the vessels of xylem. What does this observation explain?
(a) eosin solution gets stored in the xylem
(b) water moves through xylem in the plant
(c) xylem reacts with eosin and gives colour
(d) most portion of the plant stem is occupied by xylem
24. A student setup an experiment using a well-watered plant. The plant’s roots and soil were covered with a rubber sheet. The plant was then kept in a glass bell jar and sealed with Vaseline at the bottom part to prevent the flow of air. The student keeps the apparatus in the light and observes water drops inside the jar after 2 hours as shown in the image.
What can be evaluated about transpiration from this experiment?
(a) Plant leaves give off water in form of vapours.
(b) Heat from the outside warms the jar which melts the vaseline into vapours.
(c) Plant absorbs water from environment thus extra water appears on the inside of jar.
(d) Covered roots and stem of the plant decreases the temperature of jar resulting in
condensation of moisture into vapours.
Ans: (a)
25. The image shows the transport of food material inside plant body with the help of phloem.
How is food transported from phloem to the tissues according to plants need?
(a) food is transported along with the water in plant’s body.
(b) food is transported in only direction like water in the plant body through xylem.
(c) food is transported from a region with low concentration to higher concentration.
(d) Food is transported from a region where it is produced to other parts of the plants.
Ans: (d)
26. The image shows the movement of sucrose into phloem against the concentration gradient which also leads to the movement of water due to osmotic difference. This osmotic pressure allows movement of material in plant body.
References
- http://www.cbseacademic.nic.in
- NCERT Exemplar Science Class 10
- http://www.cbseacademic.nic.in/cbe/
- NCERT Science Class 10







































Nice sir very important questions
ReplyDeleteNice question
ReplyDeleteVery good questions .
ReplyDeleteVery important question sir 👍
ReplyDeleteVery very hard questions ❓❓❓✌️✌️
ReplyDeleteThanks for questions💯💯💯💯💯
Wow case study questions is so good 👍thnks
ReplyDeleteThank you
DeleteBest are here����
ReplyDeleteThank you
DeleteBest question are here 😇😇
ReplyDeleteThank you
DeleteYou are great 😘😘
ReplyDeleteThank you
DeleteNew technology teaching here
ReplyDeleteThank you
DeleteSuperb questions from superb teacher ☺😍
ReplyDeleteThank you
Delete